Polar Coordinates
- A-Level Further Maths

- Sep 18, 2020
- 2 min read
Updated: Dec 7, 2020
The Cartesian system in two-dimensions models points in terms of x and y. The polar system, however, models a point as a distance form the pole, r (generally the origin) at a certain angle from the initial line, θ (typically the positive horizontal axis). Yes, this is like the modulus-argument form of complex numbers and Argand diagrams.
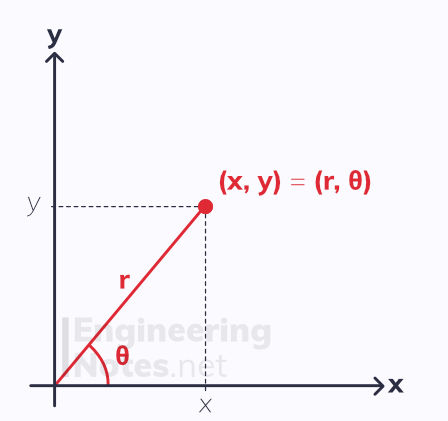
From the diagram, we can derive equations to convert between polar and Cartesian systems:
r cos(θ) = x
r sin(θ) = y
Where θ is given by:
θ = arctan(y/x)
And r is defined using Pythagoras' theorem:
r² = x² + y²
Sketching Polar Curves
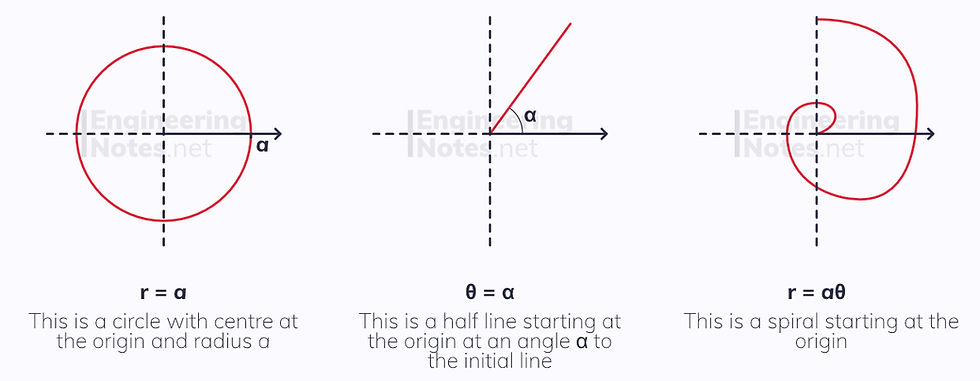
To sketch a polar curve, use a graphical calculator or draw u a table of values for regular intervals of θ. This can be done quickly using the table function on the CASIO ClassWiz fx-991EX, and we recommend using π/6 as an interval.

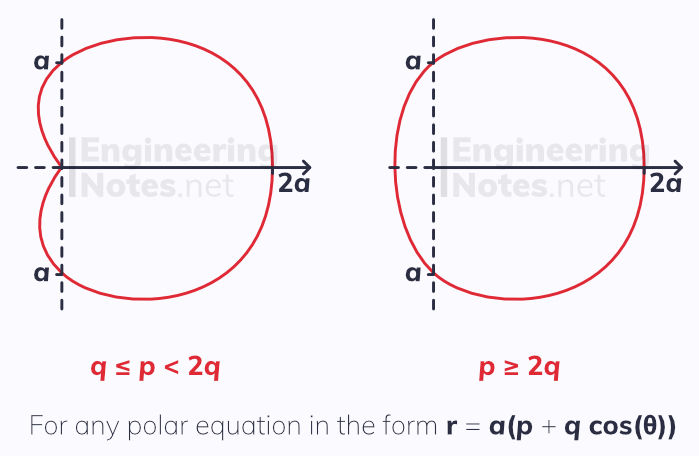
The curve in this example is known as a cardioid, due to its dimple. This is common for equations in the form r = a(p+qcos(θ)), but only if q ≤ p < 2q. When p ≥ 2q, there is no dimple, making it more egg-shaped:
Areas Enclosed by Polar Curves
The area of a sector of a polar curve can be calculated using integration. However, simply integrating r will not work. Instead:
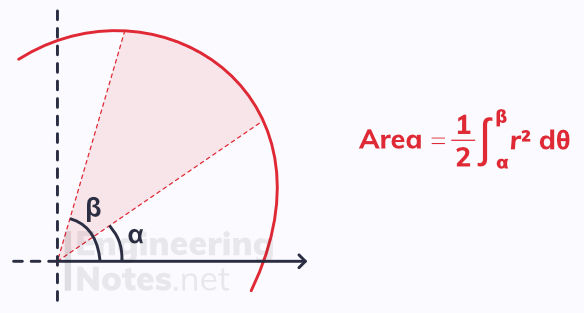
Of course, you an also calculate areas between polar curves. To do this, you need to find the angle at which they intersect.
Tangents to Polar Curves
To find tangents to a polar curve, you need to convert it into Cartesian form (one equation for x and one for y, both in terms of θ), using the formula at the top of this notes sheet. Then, you can differentiate parametrically.
Standard results are:




Comments