Nuclear & Particle Physics
- A-Level Physics

- Aug 5, 2020
- 6 min read
Updated: Dec 7, 2020
Initially, Thomson proposed the ‘plumb pudding’ model for atoms, saying the atom was made up of a blob of positive charge with negatively charged electrons sprinkled in and about this.
Rutherford’s Scattering experiment disproved this, by firing alpha particles at a gold foil and seeing where they emerged on a fluorescent screen. Most alpha particles passed straight through with very little deflection; however, some scattered a lot and others were reflected right back.
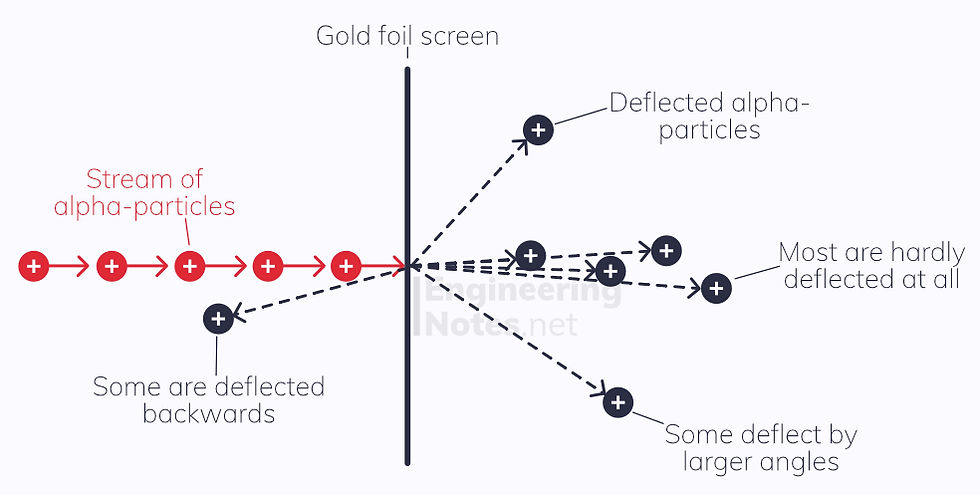
This led to the conclusion that an atom was made up of largely empty space, with a very small, very dense, positively charged nucleus in the centre. This Nuclear Model is now widely adopted:
The nucleus is surrounded by orbiting electrons in shells
The nucleus is about one 10,000th of the size of the atom, but makes up most the mass
The protons and neutrons are around 2000 times more massive than the electron
Nuclear density is always ~1017 kg m-³; atomic density is far less
Isotopes are atoms with the same proton number but a different nucleon number – the different number of neutrons does not affect the chemical properties, however can make the atom unstable.
The radius of the nucleus is directly proportional to the cube root of the nucleon number:
R = r(0) x ³√A nuclear radius = r(0) x ³√nucleon number
r(0) can be taken as 1.4 E-15
The Four Forces
There are four forces that govern the laws of physics - the strong and weak nuclear, the electromagnetic, and gravitational.
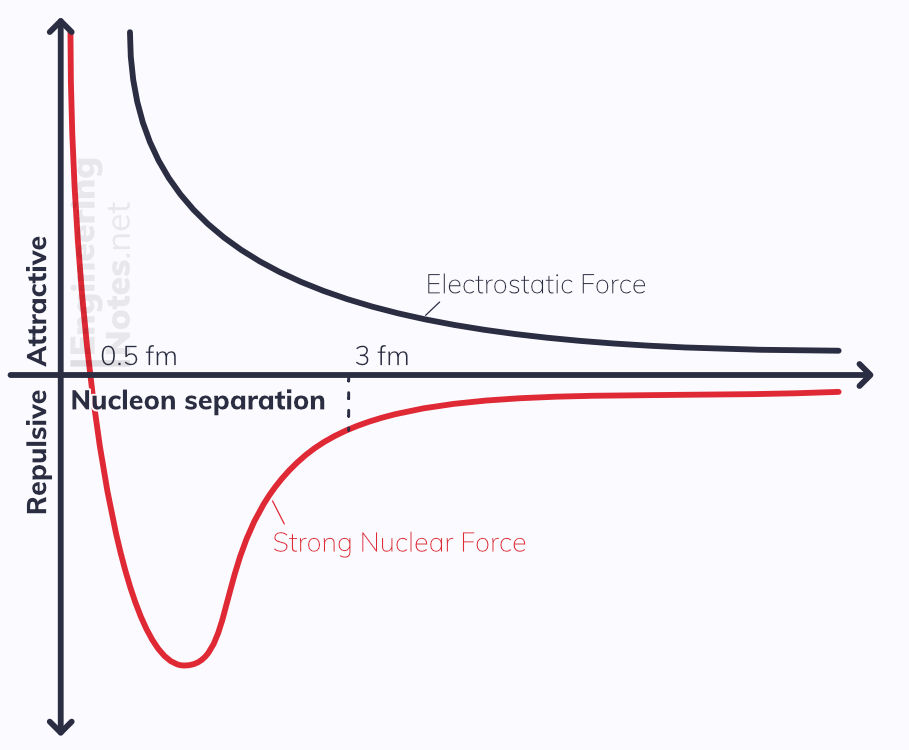
The nucleons are held together by the strong nuclear force, but as the nucleus gets bigger and the electrostatic repulsion outweighs it on the outside, the nucleus becomes unstable.
Strong Nuclear Force
Very short range: attractive to ~3 fm; repulsive to ~0.5 fm
Works equally between all nucleons
At very small separations, it must be repulsive, else the nucleus would collapse
Weak Nuclear Force
The only thing that can change one quark into another
Also very small range
Acts between all particles
Electromagnetic Force
Infinite range
Acts between all charged particles
Can be attractive or repulsive
Gravitational Force
Infinite range
Acts on all objects with mass
Always attractive
Fundamental Particles
All particles come in particle/anti-particle pairs, where each part has the same mass, but opposite charge.
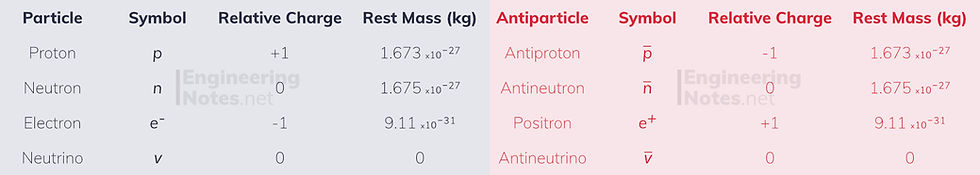
Classification of Matter
All matter is categorised into hadrons and leptons:

Quarks
The hadrons are largely made up of up, down and strange quarks, and their respective anti-quarks. All of these have a charge, and the combinations of these quarks is what gives protons their +1 and neutrons their 0 charge.
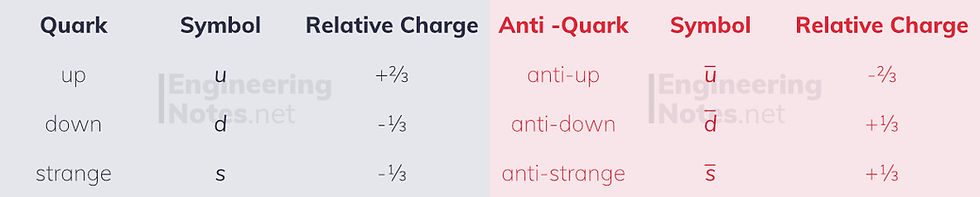
Quark notation consists of just writing the letters next to each other:
Protons are made up of uud
Neutrons are made up if udd
Decay
We can express beta decay in terms of quarks:

Radioactivity
Radioactive decay is both spontaneous (cannot be induced) and random (cannot be predicted), and typically takes one of four forms:
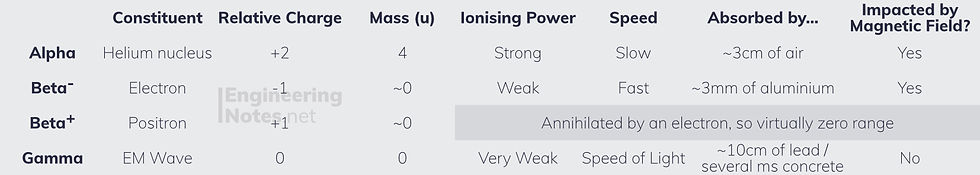
Alpha emission happens in heavy nuclei (large nucleon numbers)
Beta-minus emission happens in neutron-rich nuclei (many more neutrons than protons)
Gamma radiation is emitted from nuclei with too much energy
Half-life, T(1/2) is the average time taken for activity, mass of radioactive nuclei, or number of radioactive nuclei to halve.
The decay constant, λ, is a measure of the rate of radioactive decay.
T(1/2) = ln(2) / λ half life = ln(2) / decay constant
Activity, A, is the number of particles decaying per second.
A = λN Activity = decay constant x number of undecayed nuclei remaining
The Number of undecayed nuclei decreases exponentially (it halves for every fixed period of time, the half life).

Investigating decay
You can investigate half-life by plotting a graph of activity against time, for samples such as protactinium-234:
Shake bottle containing uranium salt, its decay products (including protactinium-234), and two solvents
Wait for two solvents to separate – the protactinium-234 will be in the top layer
Record activity of top layer
Record again every minute
Subtract background radiation from all results
Plot graph of activity against time
Determine half-life from exponential graph
Similarly, you can simulate radioactive decay with dice with one side coloured differently. Shake the pot, tip the dice on a table and remove all the ones with the coloured side facing up. Repeat this until no dice left, plotting a graph of the numbers left each round.
Carbon Dating
Radioactive isotopes can be used to date object that are more than tens of thousands of years old, using the proportion of carbon-14 in them. Plants take this in as carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and animals then eat the plants. All living things contain the same percentage of carbon-14, and using its half-life (5730 years), we can estimate something’s age by comparing current carbon-14 levels.
Mass Defect, Binding Energy & E = mc²
Einstein observed that all mass (and matter) is, in fact, energy. He relates the two with his energy-mass equation:
E = mc² Energy = mass x speed of light²
Pair Production
Pair production is when energy is converted into matter – if two photons collide with enough energy, they may create a third proton, paired with an antiproton. Typically, you get electron-positron pairs formed, because of their low mass (and therefore less energy is required).
The minimum energy the photon must have is that of the rest masses of the particle and antiparticle produced.
Annihilation
Annihilation is the opposite of pair production – all the mass of a particle and its antiparticle is converted into energy. This happens all the time, hence we do not see many antiparticles.
Mass Defect & Binding Energy
The mass of a nucleus is less than the mass of its constituent parts – the difference in mass is known as the mass defect. This is converted into energy.
The binding energy is the energy required to separate all of the nucleons in a nucleus and is equivalent to the mass defect.
The binding energy per unit of atomic mass, u, is about 930 MeV u-1
To compare binding energy on different nuclei, we look at binding energy per nucleon. This is the curve of binding energy per nucleon for all atoms:
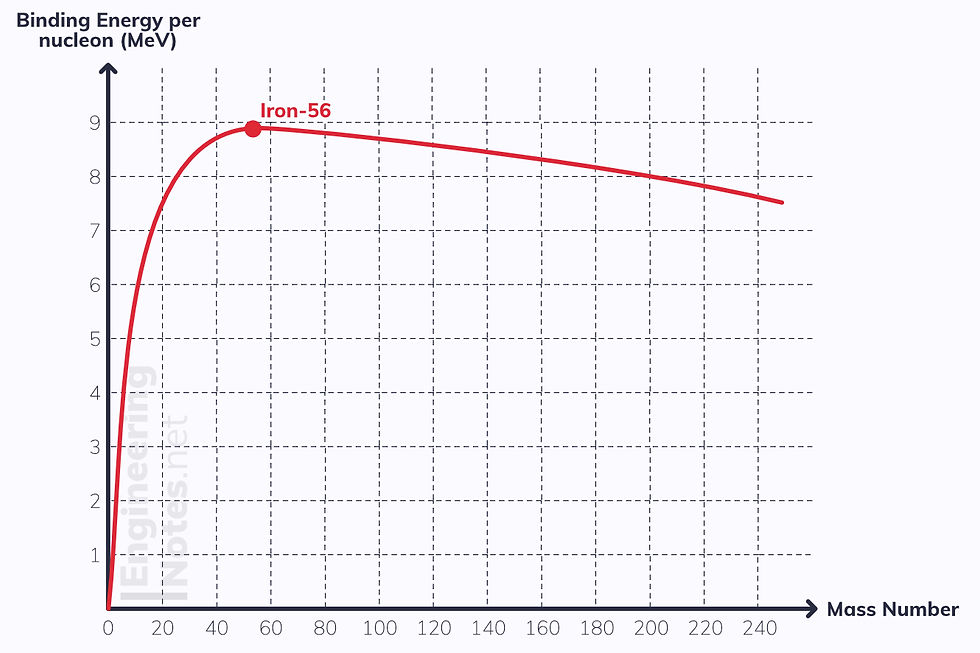
The higher the binding energy per nucleon, the more stable the nucleus, because more energy is required to remove nucleons from the nucleus
Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, as it has the highest binding energy per nucleon
Nuclei below Iron-56 will undergo fusion (which increases binding energy per nucleon dramatically, hence releases a lot of energy)
Nuclei above Iron-56 will undergo fission to split into two smaller nuclei, so binding energy per nucleon increases too, but not as dramatically as with fusion.
The change in binding energy = energy released. This is why all nuclear reactions release or require energy.
Nuclear Fission & Fusion
The Induced Fission process
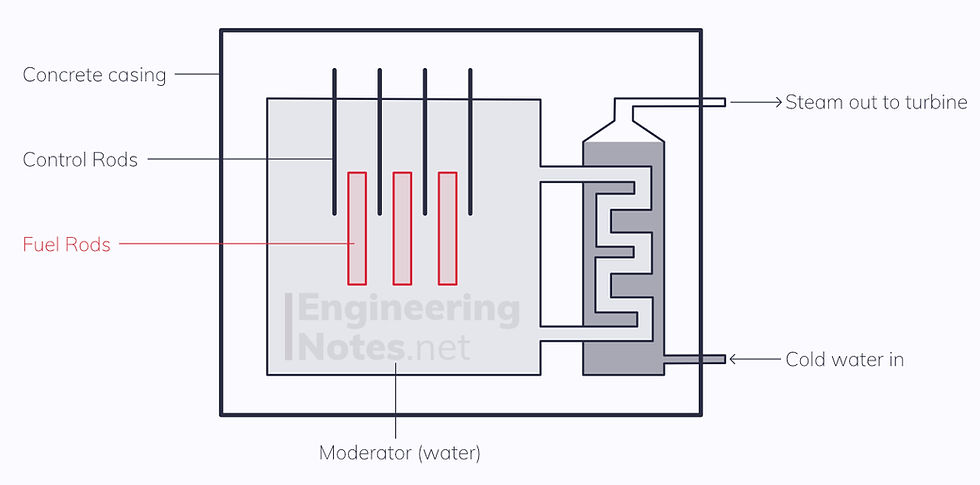
A thermal (low energy) neutron is fired at a U-235 nucleus
Uranium must be enriched, as natural occurring Uranium only has 0.7% U-235; but 2.5-3% required for fission reactions
The larger the nucleus, the more unstable
Nucleus becomes very unstable, and splits into two smaller nuclei releasing two or three fast (high energy) neutrons
The new, smaller nuclei have a higher binding energy per nucleon, and as such are more stable
The change in binding energy per nucleon means energy is released in the form of kinetic energy of neutrons
The Moderator (water) slows down the fast neutrons to be thermal neutrons, to maximise probability of starting another fission reaction
Control rods (made of boron) absorb excess neutrons, to ensure the average reaction creates one neutron for every neutron that is lost
To maintain a safe chain reaction
Critical mass is the exact mass of nuclear fuel required to keep the reaction going at a steady rate
Coolant (heavy water or CO2) around the reactor core removes the thermal energy and transfers it to the electrical generation system (turbines powered by steam)
Nuclear waste
High Level waste (used fuel rods) are stored in cooling ponds for a year before being sealed in glass blocks and buried deep in steel cases
Intermediate Level waste (empty fuel rods, old components) are encased in cement in metal drums, and stored underground.
Low Level waste (Packaging, clothes) are cleaned, compacted, placed in steel containers and sunk or buried
Nuclear Fusion
When two light nuclei have enough energy to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between them, they can get close enough for the strong nuclear force to bind them
This releases a lot of energy, because the binding energy per nucleon increases so dramatically
This energy helps maintain conditions to allow more fusion reactions to occur
A lot of energy is required to overcome the electrostatic repulsion, however
The energy released per reaction is less in fusion than in fission, but because the fusionable nuclei have such a small mass in comparison, one mole of reactants gets many, many more reactions.



Comments